Turning On Experimental Features
Docker has some nice and useful experimental features.
Unfortunately some of those, like squash are experimental since Docker 1.13.
By default, Docker Desktop (Windows Client) doesn’t have those features turned on.
To turn them on, you need to go to Settings page.
But Command Line option is not the one you are looking for.
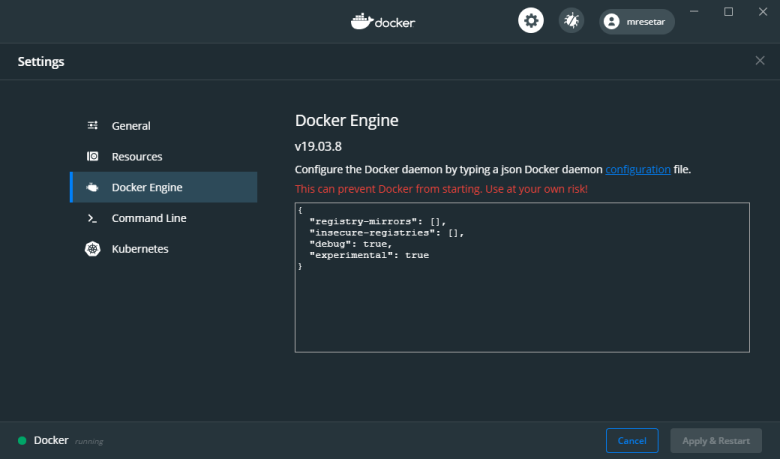
Instead, you need to make the following change on the Docker Engine page:
{
"registry-mirrors": [],
"insecure-registries": [],
"debug": true,
"experimental": true
}
You might also turn on experimental features for Command Line (above), but it is not required to.
Checking That Experimental Mode is Turned On
After Docker Engine restarts, you can open Command Prompt (WinStart + X + C) and run command
docker version -f '{{.Server.Experimental}}'
It should output 'true'.
You can also run docker version for complete output. If you see Experimental: true under Server section you
should be ready to use experimental features.
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 19.03.8
API version: 1.40
Go version: go1.12.17
Git commit: afacb8b
Built: Wed Mar 11 01:23:10 2020
OS/Arch: windows/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 19.03.8
API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12)
Go version: go1.12.17
Git commit: afacb8b
Built: Wed Mar 11 01:29:16 2020
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: true
containerd:
Version: v1.2.13
GitCommit: 7ad184331fa3e55e52b890ea95e65ba581ae3429
runc:
Version: 1.0.0-rc10
GitCommit: dc9208a3303feef5b3839f4323d9beb36df0a9dd
docker-init:
Version: 0.18.0
GitCommit: fec3683
Bonus: Using Experimental Features under WSL
It is possible, even encouraged, to use Windows Docker under Windows Subsystem for Linux (WSL). First you must be able to connect to Docker Server.
Having export DOCKER_HOST=tcp://localhost:2375 line in ~/.bashrc should do the trick.
Linux docker client should able to connect to Windows host.
After this, and having docker-ce installed. Docker version should return:
Client: Docker Engine - Community
Version: 19.03.5
API version: 1.40
Go version: go1.12.12
Git commit: 633a0ea838
Built: Wed Nov 13 07:29:52 2019
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: false
Server: Docker Engine - Community
Engine:
Version: 19.03.8
API version: 1.40 (minimum version 1.12)
Go version: go1.12.17
Git commit: afacb8b
Built: Wed Mar 11 01:29:16 2020
OS/Arch: linux/amd64
Experimental: true
containerd:
Version: v1.2.13
GitCommit: 7ad184331fa3e55e52b890ea95e65ba581ae3429
runc:
Version: 1.0.0-rc10
GitCommit: dc9208a3303feef5b3839f4323d9beb36df0a9dd
docker-init:
Version: 0.18.0
GitCommit: fec3683
To enable Client experimental features add the following in the $HOME/.docker/config.json.
{
"experimental": "enabled"
}
After this, same action could be performed using Windows command line and WSL terminal.